Framing and windowing¶
Contents
Frames extraction¶
Provides the Frames class to extract frames from raw signals
Extracts overlapping frames from raw (sampled) signals:
array ---> Frames ---> array
Examples
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from shennong.frames import Frames
Build a discrete signal
>>> a = np.arange(10)
>>> a
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
Computes frames of 3s with a shift of 1s (here we assume fs=1Hz for simplicity)
>>> f = Frames(sample_rate=1, frame_shift=1, frame_length=3)
>>> b = f.make_frames(a)
>>> b
array([[0, 1, 2],
[1, 2, 3],
[2, 3, 4],
[3, 4, 5],
[4, 5, 6],
[5, 6, 7],
[6, 7, 8],
[7, 8, 9]])
-
class
shennong.frames.Frames(sample_rate=16000, frame_shift=0.01, frame_length=0.025, snip_edges=True)[source]¶ Bases:
shennong.base.BaseProcessorExtract frames from raw signals
-
property
sample_rate¶ Waveform sample frequency in Hertz
Must match the sample rate of the signal specified in process
-
property
frame_shift¶ Frame shift in seconds
-
property
frame_length¶ Frame length in seconds
-
property
snip_edges¶ If true, output only frames that completely fit in the file
When True the number of frames depends on the frame_length. If False, the number of frames depends only on the frame_shift, and we reflect the data at the ends.
-
property
samples_per_frame¶ The number of samples in one frame
-
property
samples_per_shift¶ The number of samples between two shifts
-
get_params(deep=True)¶ Get parameters for this processor.
- Parameters
deep (boolean, optional) – If True, will return the parameters for this processor and contained subobjects that are processors. Default to True.
- Returns
params (mapping of string to any) – Parameter names mapped to their values.
-
property
log¶ Processor logger
-
abstract property
name¶ Processor name
-
nframes(nsamples)[source]¶ Returns the number of frames extracted from nsamples
This function returns the number of frames that we can extract from a wave file with the given number of samples in it (assumed to have the same sampling rate as specified in init).
- Parameters
nsamples (int) – The number of samples in the input
- Returns
nframes (int) – The number of frames extracted from nsamples
- Raises
ValueError – If
samples_per_shift == 0, meaning the sample rate is to low w.r.t the frame shift.
-
set_logger(level, formatter='%(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s')¶ Change level and/or format of the processor’s logger
- Parameters
level (str) – The minimum log level handled by the logger (any message above this level will be ignored). Must be ‘debug’, ‘info’, ‘warning’ or ‘error’.
formatter (str, optional) – A string to format the log messages, see https://docs.python.org/3/library/logging.html#formatter-objects. By default display level and message. Use ‘%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s’ to display time, level, name and message.
-
set_params(**params)¶ Set the parameters of this processor.
- Returns
self
- Raises
ValueError – If any given parameter in
paramsis invalid for the processor.
-
times(nsamples)[source]¶ Returns an array of (tstart, tstop) times of each frames of a signal
- Parameters
nsamples (int) – The number of frames of the considered signal
- Returns
times (array, shape = [nframes, 2]) – The start and stop times of each frame extracted from nsamples samples.
-
boundaries(nframes)[source]¶ Returns an array of (istart, istop) index boundaries of frames
- Parameters
nframes (int) – The number of frames to generate
- Returns
boundaries (array, shape = [nframes, 2]) – The start and stop indices of each frame extracted from nsamples samples.
-
make_frames(array, writeable=False)[source]¶ Returns an array divided in frames
- Parameters
array (array, shape = [x, ..]) – The array to be divided in frames
writeable (bool, optional) – Default to False. When True, the returned array is writable but the frames are made of copies of the original array. When False, the result is read-only but this optimizes the process: no explicit copy is made of the orignal array, only views are used. (see https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy-1.15.0/reference/generated/ numpy.lib.stride_tricks.as_strided.html)
- Returns
frames (array, shape = [nframes(x), samples_per_frame, …]) – The frames computed from the original array
-
property
Windows functions¶
Implementation of different types of window functions
This is usefull when computing frames for features extraction. Uses the kaldi implementation.
The implemented window functions 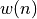 are, with length noted
are, with length noted
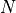 :
:
rectangular:
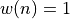
hanning:
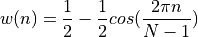
hamming:
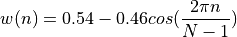
povey (like hamming but goes to zero at edges):
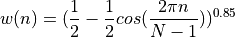
blackman, with blackman_coeff noted as
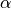 :
: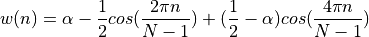
Examples
>>> from shennong.window import window
>>> window(5, type='hamming')
array([0.08, 0.54, 1. , 0.54, 0.08], dtype=float32)
>>> window(5, type='rectangular')
array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.], dtype=float32)
>>> window(5, type='povey').tolist()
[0.0, 0.5547847151756287, 1.0, 0.5547847151756287, 0.0]
-
shennong.window.window(length, type='povey', blackman_coeff=0.42)[source]¶ Returns a window of the given type and length
- Parameters
length (int) – The size of the window, in number of samples
type ({'povey', 'hanning', 'hamming', 'rectangular', 'blackman'}) – The type of the window, default is ‘povey’ (like hamming but goes to zero at edges)
blackman_coeff (float, optional) – The constant coefficient for generalized Blackman window, used only when type is ‘blackman’
- Returns
window (array, shape = [length, 1]) – The window with the given type and length
- Raises
ValueError – If the type is not valid or length <= 1